585 views Yuda Electronic (HK) Technology Co.,Limited. 2018-12-18
The charger method for smart devices is about to change dramatically. By 2024, shipments of smartphone wireless charger systems are expected to exceed 1 billion units per year.
Consumer market is the key to global growth in wireless charger technology
According to Memes Consulting, in recent years, from the integration of smart phones to Starbucks coffee shops, wireless charger technology has attracted widespread attention in the industry. However, the development of the wireless charger market will remain very unbalanced and will be mainly oriented to the consumer sector: for example, by 2024, consumer wireless charger receivers in smartphones are expected to exceed 1.2 billion, but electric and hybrid Wireless chargers for electric vehicles (EV/HEV) are not expected to be available in the market until 2022.

Wireless charger vs wired charger
The general consumer market has the greatest demand for wireless chargers, which is related to the popularity of consumer electronics such as smart phones, smart headsets, and smart watches, which require frequent charging. Since wireless chargers are still an “early” market demand, wireless chargers are growing faster than expected.
Technology developers and phone accessories suppliers/manufacturers have jointly promoted the application of wireless charger technology, not only creating new markets, but also rapidly cultivating the market. Wireless chargers are now available in smart furniture, airports and restaurants. In the future, as mobile phone manufacturers such as Apple will push more wireless smart devices to the mass market, they may become the future standard in the future.
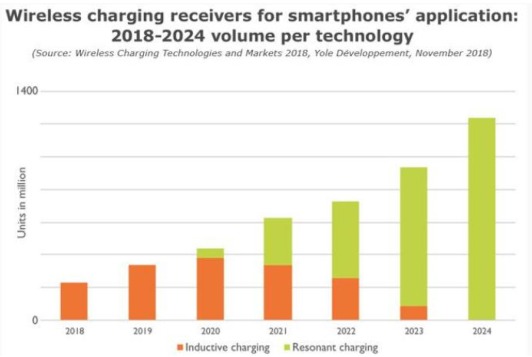
Two technologies in the wireless charger industry
For consumer electronics and future mobile applications, only two technologies are expected to be commercially available in the next five years: inductive chargers and electromagnetic resonant chargers. These two methods are technically similar, but their characteristics vary widely.
The inductive charger requires coupling between the transmitting coil and the receiving coil, thus requiring the transmitter and receiver to be in close proximity to each other. This charger technology discards the cable, but in the process of the charger, there is no flexibility, and the phone needs to be limited to a certain position. However, due to its maturity and relatively high efficiency, this is currently the only viable business option. Mobile phone makers such as Apple are working hard to increase the efficiency of this technology’s chargers before moving on to the next stage of wireless charger technology, the electromagnetic resonant wireless charger.
With an electromagnetic resonant charger, this device can be used at greater distances from the charger area, thus increasing the freedom of the charger position. The new charger technology is expected to be used soon in consumer electronics, and its existing prototypes can be used with phones that support the Qi standard. Unfortunately, electromagnetic resonant chargers are still not mature enough and are inefficient, and these two shortcomings limit their market applications.
Despite these shortcomings, the potential of electromagnetic resonant chargers continues to provide an attractive market for GaN component manufacturers. It depends on whether the industry will switch from the current 105KHz~205kHz band to a higher signal frequency.
Other technologies such as capacitive wireless chargers, laser chargers, and microwave chargers are still experimental and limited to very specific applications such as military or aerospace. It is unlikely that we will soon see these technologies successfully entering the consumer product arena.
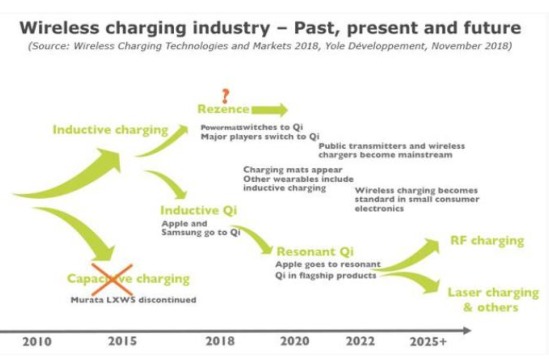
Technology developers have effectively solved the complex technical problems of smart phones placed in strong electromagnetic fields, and in just a few years, a complete industry chain focused on mobile phone inductive chargers has already been implemented.
It is worth noting that the value chain of the inductive charger is very similar to the developing electromagnetic resonant charger. In fact, the two are very similar in terms of technical content: they are all composed of inverters, rectifiers, drivers, buck converters and coils.
In fact, most industry players are developing products for both technologies. For example, Infineon Technologies offers samples of 6.78MHz electromagnetic resonant charger components and also provides 105-205kHz inductive charger semiconductor components.
Although the wireless charger application is still in its infancy, the industry chain has been solid and large semiconductor companies have provided the best electronic components.

Cell phone accessories wholesale business can get high profits. But the market is fierce. Big bra...

Does fast charging reduce phone battery life? In order to allow everyone to understand this matt...

How to install the car charger: 1. Insert the USB power adapter into the car cigarette lig...